Chlorhexidine is a cationic antiseptic widely used for the control of bacterial plaque. Its molecule was developed during the 1940s by Imperial Chemical Industries as a topical antiseptic. Later, in the 70's, Löe and Schiott made their anti-plaque and anti-gingivitis properties known.
Today, Chlorhexidine is the antiseptic of reference for its high efficacy and safety.
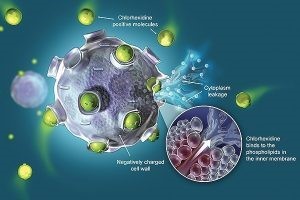 The cationic condition of chlorhexidine explains its broad-spectrum efficiency against gram-positive bacteria, gram-negative bacteria, viruses and fungi. The binding of chlorhexidine to the negatively charged cell wall of the microorganism destabilizes its structure and causes its death.
The cationic condition of chlorhexidine explains its broad-spectrum efficiency against gram-positive bacteria, gram-negative bacteria, viruses and fungi. The binding of chlorhexidine to the negatively charged cell wall of the microorganism destabilizes its structure and causes its death.
What is the mode of action of chlorhexidine?
The positively charged chlorhexidine molecule is also able to bind to other structures such as hydroxyapatite in tooth enamel, dental plaque and some negatively charged salivary proteins.
This causes chlorhexidine to be released progressively into the oral cavity over 8-12 hours with prolonged action (substantivity).
Can it cause tooth discoloration?
Continued use of the substance and contact with certain beverages and foods such as red wine, coffee and also tobacco can cause discoloration of the teeth, which is known as extrinsic staining or discoloration.
Such discoloration is believed to be caused by the precipitation of substances containing these types of foods and beverages known as chromogens and may range from white stripes to yellow dyes or brown spots.

It should be noted that this type of staining can be easily removed with a professional prophylactic technique.
In addition to the diet consumed, the degree of staining is also affected by the chlorhexidine concentration of the product. In dentistry, 2 concentrations of chlorhexidine rinses are available: 0.20% and 0.12%. Both concentrations are effective in terms of plaque and gingival index reduction, although the staining area and intensity is significantly higher when using the 0.20 % chlorhexidine concentration. Maintain a healthy mouth with daily care routines.
Discover our products for daily oral care

Over the years, various attempts have been made to develop "non-staining chlorhexidine mouthwashes"However, all chlorhexidine mouth rinses that included the antidecolorization system were ineffective against gingivitis. Thus, the evidence seems to imply that staining is an unavoidable effect if we really want to make the Mouthwash antiseptic.
[i] [ii]
Despite the possibility of this type of staining, which can be minimized by controlling food intake and the duration of treatment, Chlorhexidine remains the antiseptic of choice in oral care, as it prevents complications and therefore ensures the effectiveness of the treatment.
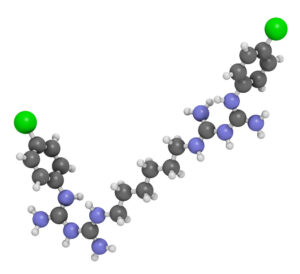 Chlorhexidine:
Chlorhexidine:
Cationic molecule with 2 groups (+) that produces non-specific bonds to surfaces (-):
- Microorganisms: ANTISEPTIC PROPERTIES
- Oral surface: SUBSTANCE
Chlorhexidine's staining ability is inherent in its chemical structure which also provides antiseptic and substantive properties.
Discover our oral hygiene products with CPC
You may be interested in: Cetylpyridinium chloride as a tool against COVID-19
Suggested Reading on Chlorhexidine
[i] Balagopal S, et al. Chlorhexidine: The Gold standard antiplatelet agent. J Pharm Sci & Res. 2013; Vol 5(12): 270-274.
[ii] Guggenheim B and Meier A. In vitro effect of chlorhexidine mouth rinses on polyspecies biofilms. [In vitro effect of chlorhexidine mouthwashes on poly-species biofilms] Res & Sci. 2011; 121(3): 432 - 436.
From Laboratorios KIN we encourage you to send us any doubt or question about this substance through the comments.
Follow us: Facebook, Twitter, Linkedin or Instagram
 How to relieve pain with newly placed braces?
How to relieve pain with newly placed braces? How to keep your breath fresh?
How to keep your breath fresh? 10 Tips to take care of the oral health of the little ones
10 Tips to take care of the oral health of the little ones