9
Patents
National and international
More than 50 years of smiles
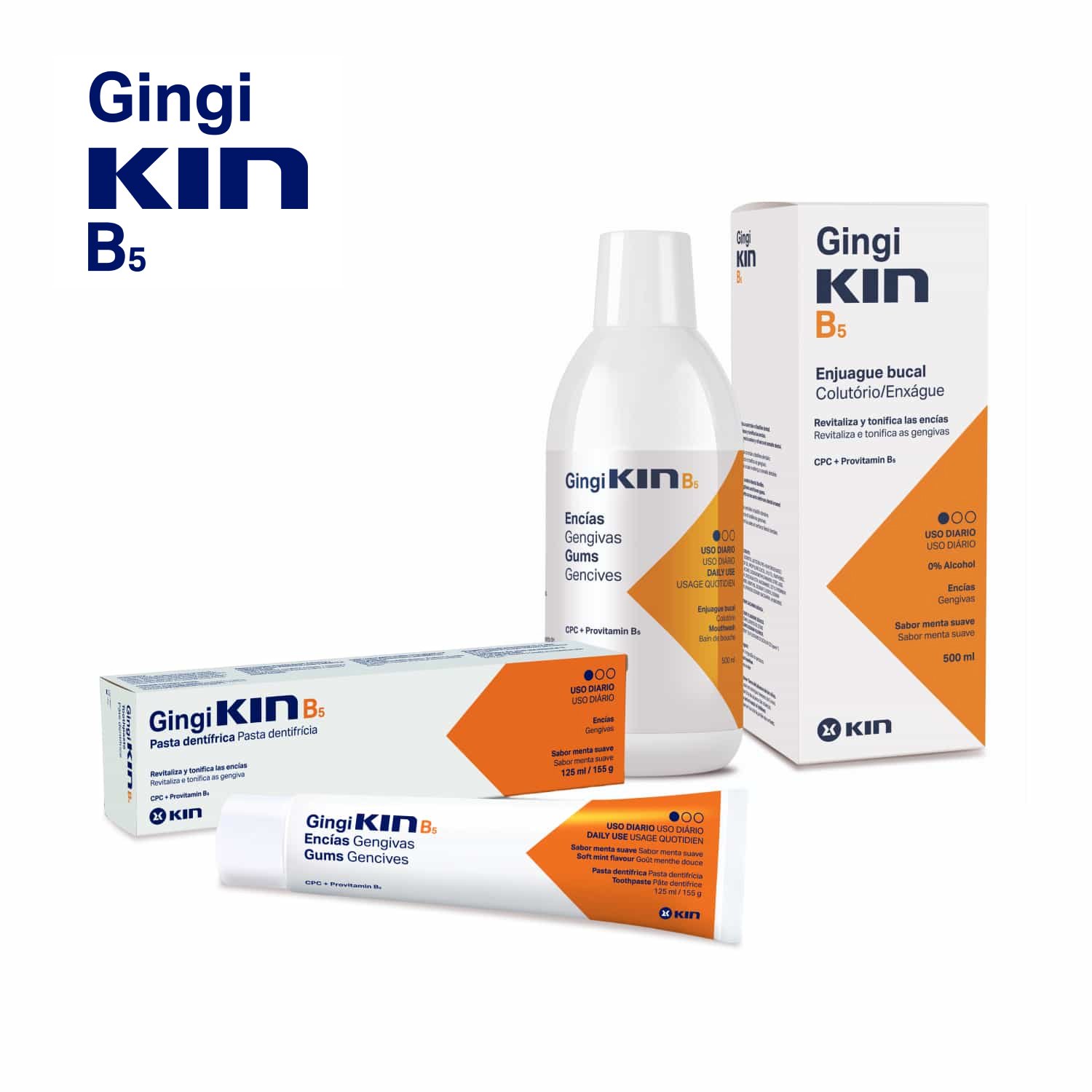
Toothpaste and mouthwash for daily care.
More information



9
Patents
National and international
+60
Countries
Where KIN products are present
+35
Lines
Of oral care products
-225
Tons of CO2
Annual savings, thanks to digitalization and reduction of travel time